Physiotherapy treatment — from 200 UAH per day
What is an intervertebral disc herniation or an intervertebral hernia?
An intervertebral hernia is a process of protrusion (complete or partial) of the intervertebral disc outside the vertebral space with or without rupture of the fibrous ring. This phenomenon is accompanied by degenerative changes in the disk: a decrease in the height of the disk and the deposition of salts.
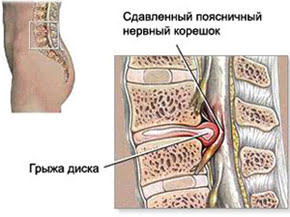
What happens when an intervertebral disc herniation forms?
The formation of a hernia leads to compression of the nerve root and blood vessel. At the same time in the nerve root there is an inflammatory process of aseptic nature, accompanied by pain, motor and sensory disorders. Discogenic radiculopathy or radiculoischemia occurs.
What are the complaints of a patient with an intervertebral hernia?
First of all, acute extremely severe pain, significant restriction of movements in the neck - if a hernia in the neck or lower back and leg - if a hernia in the lumbar region. Very often numbness of the arm or leg, respectively, restricted movement, muscle weakness.
Which doctor to see if an intervertebral disc herniation is suspected? As a rule, you should consult a neurologist, after which further tactics will become clear: - What necessary examinations should be performed on the patient? CT? MRI? With contrast or without… - which part of the spine CT or MRI?
Patients often make mistakes by doing examinations beforehand. As a rule, the error is the inconsistency of the MRI or CT examination area to the anatomical area of hernia formation. pain gives in the interscapular area, in the arm, in the chest. Such patients often bring a CT or MRI of the shoulder joint or chest… And this is an additional cost… It is worth starting with a neurologist! The neurologist draws up an individual examination plan for each patient, establishes the diagnosis and chooses treatment tactics according to the patient's condition: medication, physiotherapy, consultation with a vertebrologist-rehabilitation specialist, neurosurgeon, rehabilitation. fixation - skew of the torso, reduce the manifestations of sensory and motor disorders… This is the first part of treatment.

When do you need to consult a neurosurgeon?
If a neurologist detects a rapidly progressing neurological deficit: rapidly increasing numbness or muscle weakness in the arm or leg that progresses significantly during the day; perineal numbness; urinary retention or incontinence; gait disorders… Large hernia with the phenomena of stenosis of the spinal canal or neuronal - foraminal opening according to MRI…
When do you need a consultation with a vertebrologist-rehabilitation specialist?
After the removal of acute pain, reduction of muscle tension, increase in the volume of free movements in the neck or lumbar region, it is necessary to begin the second part of treatment: selection and training of therapeutic gymnastics; selection of Schantz fixing collars or orthopedic posture correctors, which provide an opportunity to reduce the vertical load on the cervical and lumbosacral spine, respectively. This is extremely important, especially if the patient has a persistent muscular-tonic syndrome with pathological fixation of the cervical or lumbar spine of the kyphoscoliotic type - persistent skew of the cervical or lumbar spine. The doctor also selects foot correctors based on plantoscopy!!!
What are the methods of treating disc herniation in Health Practice?
Our clinic has many years of experience, which allows for successful conservative treatment of intervertebral hernias. In a complex of therapeutic and treatment-rehabilitation procedures in the treatment of patients with intervertebral hernia of varying severity, we combine modern physiotherapy techniques of different spectrum of action, drugs with anti-edema, anti-inflammatory, muscle relaxant, vegetative stabilizing, anti-vascular, anti-inflammatory, acupuncture, pharmacopuncture, laser acupuncture, electrotherapy with therapeutic exercises. The approach to each patient is always individual.
The key to successful treatment of intervertebral disc herniation is a timely visit to the doctor, a comprehensive approach to treatment, compliance with the regime of therapeutic exercises and a plan of preventive measures.
