Physiotherapy treatment — from 200 UAH per day






What is Tunnel Syndrome or Compression Ischemic Neuropathy?
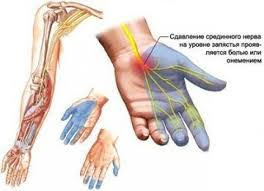
Compression ischemic neuropathy or tunnel syndrome refers to a group of diseases, the main cause of which is the compression of the nerve root, blood vessel or vascular nerve bundle at the sites of anatomic narrowing (tunnels), bone-fibrous or fibrotic ulcers, apical beds, apical beds, The mechanism of development of CIN begins with overstrain of the ligaments and muscles around the nerve end, compression and stretching of the nerve. The following phenomena are swelling and aseptic inflammation of the tendons, yzvodyt walls to the proliferation of channels and hyperplasia of connective fibrous tissue at fixing tendons to bone vystupiv.Rozvyvayetsya osteofibroz
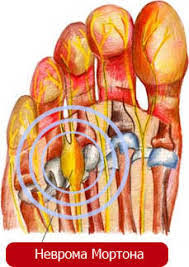
What factors lead to tunnel syndrome or compression ischemic neuropathy?
- osteochondrosis with neurodystrophic syndrome
- congenital narrow canal or anomaly of canal development
- pathology of the endocrine system (acromegaly, hormonal contraception, lactation, hypothyroidism, menopause)
- deformation of the tunnel after injury
- chronic injury (occupational microtraumatism overload)
- tumor formation
- systemic diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, myeloma, amyloidosis)
- atrophy of subcutaneous fat, exhaustion
What types of compression-ischemic neuropathy distinguish?
There are acute and chronic compression-ischemic neuropathy.
What are the main clinical signs of compression ischemic neuropathy?
Consider the main clinical features of compression-ischemic neuropathy:
| Group 1 Local changes |
Tension, tenderness, hypo- or hypertrophy of certain muscles, which is determined by palpation, pain in projection of the nerves |
| Group 2 Neurological disorders |
Changes in the sensitivity of the distal painful tunnel, hypalgesia, paresis of the tendon or foot, individual fingers, muscle atrophy |
| Group 3 Vegetative-vascular disorders |
Trophic disorders in the area of regional innervation: changes in color and temperature of skin, nails, hair, sweating disorders |
What are the possible options for the development of compression-ischemic neuropathy?
There are 2 options for the development of CIN:
- with the advantage of demyelination processes
- with a predominance of vasomotor disorders
What are the stages of compression-ischemic neuropathy?
There are 4 stages of compression-ischemic neuropathy:
- Irritative - acute CIN
- Irritative-deficient-subacute CIN
- Deficient - chronic CIN (electrophysiological indicators reduced)
- Deficit-dystrophic CIN (electrophysiological indicators are significantly reduced or absent)
What examinations should a patient undergo with suspected compression ischemic neuropathy? Examination of patients combines anamnesis collection, neurological examination with obligatory use of tests: Tinnell, cuff, turnstile, elevator; radiography of the relevant sites, MRI, ENMG.
What is the treatment of patients with compression-ischemic neuropathy?
The treatment of patients in "Health Health I" consists of drug therapy:
anti-edema, anti-inflammatory, venotonics, analogues of GABA, metabolic and antihypoxant therapy, anticholinesterase, B6 vitamins with B6 composition, hormonal or novocaine blockade, local resorption therapy, muscle relaxants, dehydrating therapy and dehydrating therapy.
Physiotherapy treatment and reflexology
Magnetic therapy with variable or pulsating MP
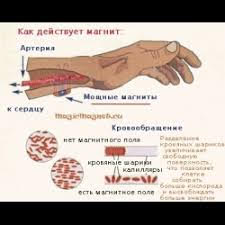

What is the use of magnetotherapy?
The use of magnetotherapy is shown at all stages of the development of CIN, especially in acute! The rationale is pronounced anti-edema, anti-inflammatory action, mediated stimulation of venous outflow, improvement of rheological properties of blood.
Magnetotherapy can be the main method of treatment of CIN, since its effectiveness in subacute stage and in the process of chronic process is proved. In cases of pronounced phenomena of disturbance of microcirculation (local venous stagnation, edema, lymphostasis) we use the frequency 10Hz. Magnetic Induction Options - Individual Selection! The course of treatment with daily regimen - up to 7 days.

Laser therapy and laser puncture, quantum therapy
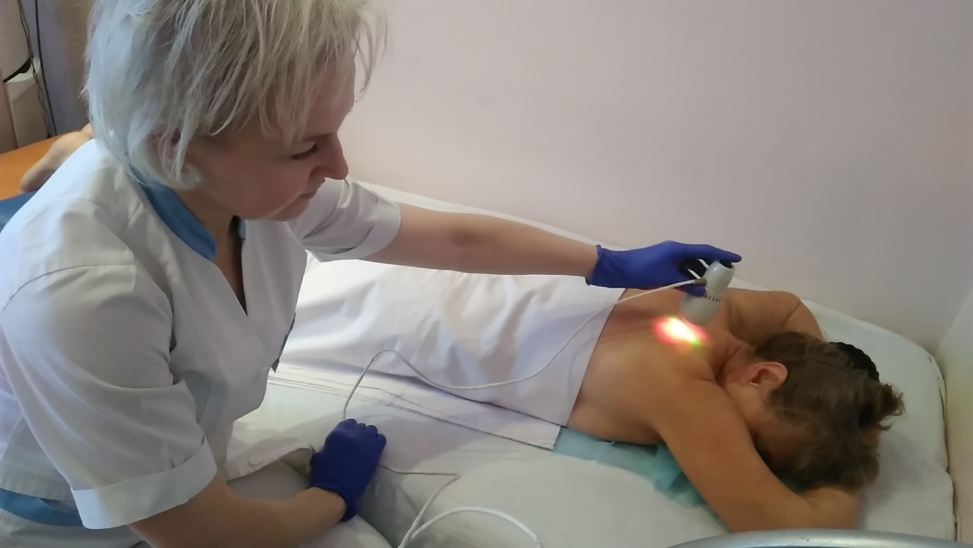
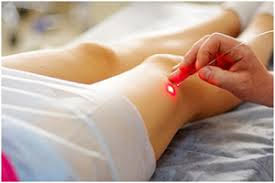
What is the rationale for the use of laser therapy?
The use of laser therapy is based on the features of the action:
biostimulant effect, improvement of microcirculation at the tissue and cellular level, anti-pain, anti-edema and trophotropic action.
We apply red (wavelength 0.63 μm) and infrared LV (wavelength 0.78-0.9 μm). Laser therapy is shown at all stages of CIN. Exposure 7-10 minutes.
What are the features of laser therapy?
The peculiarity of laser therapy is the possibility of the combined application of the procedure directly to the projection of CIN and segmental to segmental areas of the spinal cord.
In the case of upper extremity CIN, laser therapy is released for the projection of C8-Th2-Th4 segments
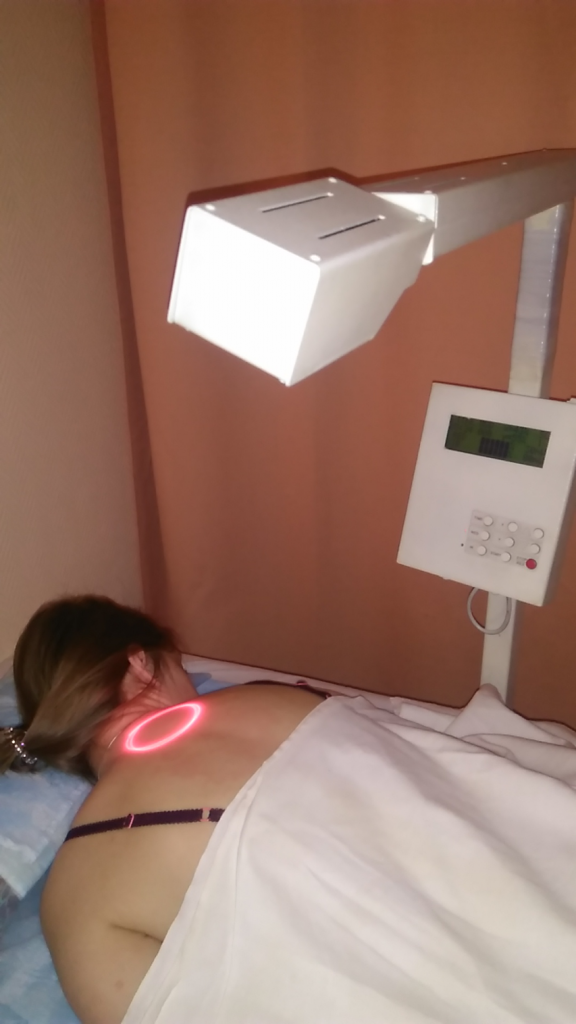
and in the case of the lower extremity CIN, the projection of the Tn12-11-12 segments.
Acupuncture causes local excretion of enkephalins and endorphins, which at the level of the neuron affect the K-Na pump by reducing the penetration into the cell of sodium ions. impulses from the problem organ.
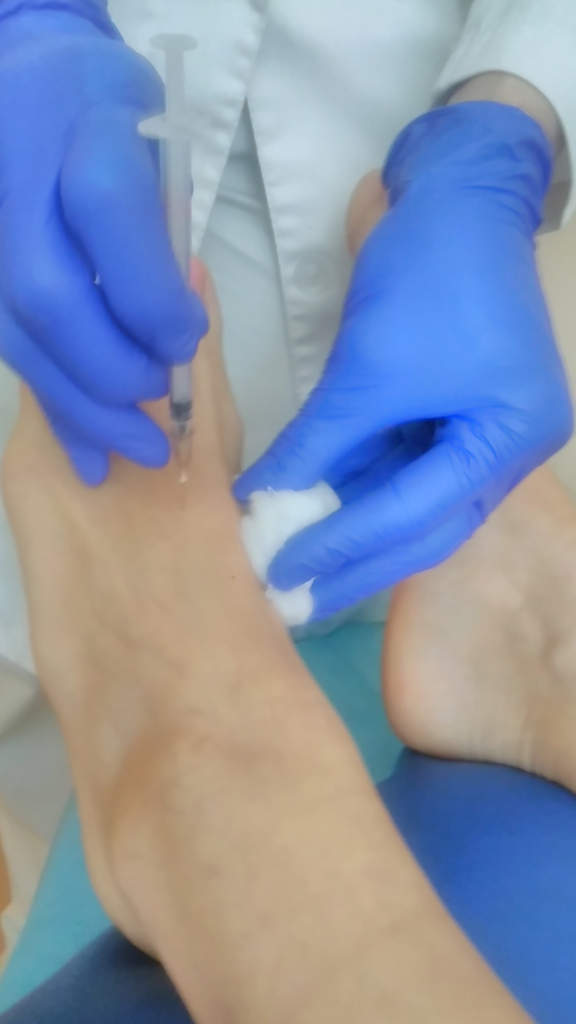
Pharmacopuncture - introduction of small doses of medicines into biologically active points, is considered highly effective at the initial stages of CIN and prospective at 3 CIN stages)
Current electrotherapy and electropuncture with the use of acupuncture points (TA) in the course of the affected nerve. Time exposure and parameters are assigned individually. Treatment period 10 days.
The long-term medication is obligatory to use pregabalins, gabapentins, calcium channel blockers, novocaine and hormonal blockages, postisometric relaxation and kinesitherapy
If ineffective, surgical treatment is recommended.
